Oracle 模式对象
模式是与每个Oracle数据库用户相关的一组数据库对象的集合。 模式所有者拥有该模式下所有数据库对象,如表、视图、索引、同义词、数据库链接、过程、函数、和包等的全部权限。
模式对象是由用户创建的逻辑结构,用以包含或引用他们的数据。模式对象包含诸如表、视图、索引子类的结构
A schema is a collection of database objects. A schema is owned by a database user and has the same name as that user. Schema objects are logical structures created by users. ... You can create and manipulate schema objects with SQL or with Oracle Enterprise Manager.
These are Tables, Indexes, Views, Synonyms, Sequences, Database Links, Directory Objects, and Reorganize Objects.
Note: There is no relationship between a tablespace and a schema. Objects in the same schema can use storage in different tablespaces, and a tablespace can contain data from different schemas.
- Oracle schema = Oracle user + database objects owned by that user.
- When an Oracle user is created using the CREATE USER command, a schema gets created for the user by default.
- There is a one-to-one correspondence between Oracle user name and Oracle schema name.
- While user = schema in most circumstances, that isn’t true all the time.
数据字典
是表和相关视图的集合,包括静态数据字典和动态性能数据字典
1. 静态数据字典
- 模式对象的定义(模式对象是由用户创建的逻辑结构)
- 完整性约束
- 权限和角色
- 为模式对象所分配的存储空间
- 数据库操作审核信息
分为
- 用户视图:
USER_xxx,包含当前用户所拥有的全部对象 - 扩展用户视图:
ALL_xxx,包含当前用户当前可以访问的全部的对象和权限的信息 - 数据库管理员视图:
DBA_xxx,包含了数据库拥有的所有对象和权限的信息
-- 查询d_xxx数据字典结构
desc d_xxx;
-- 查询用户alex在数据库拥有的所有模式对象信息
select * from user_objects;
-- 查询用户alex的表t_abc的结构定义信息
select column_name from user_tab_columns where table_name='T_ATTEND_D312'; -- AD一定要大些、写
-- 查询表的存储参数
select * from user_tables where table_name='xxx';
-- AD xxx必须不是同义词且必须大写
-- 查询alex权限授予情况
select * from user_tab_privs;
-- 查询数据字典`recyclebin` 来了解该表是否在回收站中
select * from recyclebin where origin_name='t_xxx'
-- 查询当前用户创建的同义词
select * from user_synonyms;
-- 查询视图定义
select * from user_views where view_name=upper('v_xxx');
-- 查询可更新视图中哪些列可以更新
select * from user_updatable_columns where table_name='v_xxx';
-- 查询当前创建的序列信息
select * from user_sequences;
-- system模式下显示所有者是u_lzc的所有索引对象
select * from dba_indexes where owner='u_lzc';
-- 显示索引列
select * from user_ind_columns where index_name='idx_x';
-- 显示索引段的位置及大小
select * from user_segments where segment_name='idx_xx';
-- 显示函数索引
select * from user_ind_expressions where index_name='x';
-- 在system模式下,从dba_data_files数据字典中查询表空间及其包含的数据文件
select * from dba_data_files;
-- 查询users表空间内存放的数据对象及其类型和拥有者
select * from dba_segments where tablespace_name='USERS';
-- 查看表空间的数据文件
select name from v$datafile;
-- 查看用户表空间
select default_tablespace, temporary_tablespace from dba_users where username='C##U_LZC_D312';
-- 查看系统默认表空间
select property_value from database_properties where property_name='DEFAULT_PERMANENT_TABLESPACE';
-- 查询环境资源字典及其限制
select * from dba_profiles order by profile;
-- 查看系统权限
select * from user_sys_privs;
-- 查看授予xx用户的所有权限
select * from dba_tab_privs where grantee='C##U_LZC_D312';
-- 查询预定义角色的细节
select * from dba_sys_privs where grantee='C'
2. 动态数据字典
动态性能表记录当前数据库的活动情况和性能参数
在动态性能表的基础上创建了动态性能数据字典视图,通常称为V$视图
-- 可出当前所有后台进程及其运行错误
select name, description, error from V$BGPROCESS;
-- 查看日志文件信息
select * from v$log;
表
1. 数据类型
- 字符:
char,varchar2 - 数值:
number(5,2),int - 日期:
date - LOB 数据类型(大型的,未被结构化的数据):
blobclobbfile ROWID
2. 约束
2. 1 约束类型
-
非空约束:
not null(col_name) -
主键约束:
primary key(col_name) -
唯一性约束:
unique(col_name) -
外键约束:
foreign key(col1) references t_xxx(col2)
若外键列与被引用表的被引用列同名,则可以写成
foreign key(col) references t_xxx
- 检查约束:
check(sex in ('男', '女'))
PS:对于非空约束与主键约束,若该表已存在数据,但不满足该约束,则该约束操作将失败
PS:当尝试删除外键约束中被引用表的一行时,可通过on关键字指定处理方案foreign key(col1) references t_xxx(col2) on ???中,???有以下三种类型
no action:默认,禁止删除该行set null:外键表中的外键列全部设为null,前提是外键列必须支持null值cascade:级联操作,例如delete cascade表示外键表中相应的数据也被删除
2. 2 创建约束
-- 单独写一行
constraint cst_xxx 约束类型表达式
constraint cst_xxx primary key(col_name)
-- 写在字段声明后面
-- 匿名
sno char primary key
mno char references t_xxx(col2)
sex char check(sex in ('男', '女'))
birthday date check(birthday between date '1994-01-01' and date '1999-07-31')
-- 有名
-- sno char constraint cst_xxx primary key
-- alter语句
alter table t_xxx add constraint cst_xxx 约束类型表达式
alter table t_xxx add constraint cst_xxx foreign key(col) references t_yyy
2. 3 激活/禁用约束
禁用
-- 写在字段声明后面
sno char primary key disable
-- 禁用已存在的约束:alter
alter table t_xxx disable constraint cst_xxx;
PS:
- 禁用主键约束时,Oracle会默认删除约束对应的唯一索引,激活时自动重新建立;若不希望这样,可以在禁用约束时使用关键在
keep index(通常放在约束名后面) - 禁用唯一性约束或主键约束时,如果有外键约束正在引用该列,则可以先禁用该外键约束,再禁用它;或者在禁用唯一性约束或主键约束时,使用
cascade,这样可以级联禁用
激活
novalidate:不检查数据表中已存在的字段是否满足validate:默认,检查...
-- 激活已存在的约束:alter
alter table t_xxx enable [novalidate | validate] constraint cst_xxx;
2. 4 删除约束
alter table t_xxx drop constraint cst_xxx
3. 创建表
create table t_xxx
(
col1 int default 0,
col2 char default 'xxx' col_constraint,
constraint_1,
constraint_2
)
-- 复制表的结构
create table 新表 as
select * from 旧表 where 1=2;
-- 也复制表的相关内容
create table 新表 as select * from 旧表
-- 将查询结果插入另一张表
insert into 已定义的表
select * from ...
在自己模式中创建表必须拥有create table系统权限
在其他用户模式中创建表必须拥有create any table系统权限,此外必须在表名前加上某个模式的名称,如scott.t_xxx
创建好后可以通过desc t_xxx查看表的数据结构
4. 增加和删除字段
-- 增加
alter table t_xxx add(sno char);
-- 删除
alter table t_xxx drop column sno;
alter table t_xxx drop column (sno, sname);
-- 修改
alter table t_xxx modify col_xxx 属性
-- AD 对先前已插入的数据并不起作用
5. 重命名表
alter table t_xxx rename to t_yyy;
6. 表空间和存储参数
create语句后面可加上以下可选的语句
create (...)
pctfree n -- 块内预留自由空间百分数 默认10
pctused n -- 块内已使用空间最小百分比
initrans n -- 表的每个数据块中分配的事务项初值,默认1
maxtrans n -- 可同时修改表的数据块的最大事务数
recoverable | unrecoverable
tablespace ts_xxx
enable | disable
as query
nologging -- 对DDL操作产生日志数据
cache | no cache
storage n -- 分配给表的存储空间大小
-- 修改表的状态/参数
alter table t_xxx pctfree 25 pctused 45;
7. 删除表
drop table t_xxx [cascade constraints]
cascade constraints:删除关联的触发器、视图、约束等
一般情况下,删除表只是在数据字典里除名,实际依然占用存储空间。此时可利用flashback table语句还原
flashback table t_xxx before drop
8. 修改表的状态
alter table t_xxx read only;
alter table t_xxx read write;
索引聚簇表
- 聚簇是指:如果一组表有一些共同的列,则将这样一组表存储在相同的数据库块中;聚簇还表示把相关的数据存储在同一个块上。利用聚簇,一个块可能包含多个表的数据。概念上就是如果两个或多个表经常做链接操作,那么可以把需要的数据预先存储在一起。聚簇还可以用于单个表,可以按某个列将数据分组存储。
更加简单的说,比如说,EMP表和DEPT表,这两个表存储在不同的segment中,甚至有可能存储在不同的TABLESPACE中,因此,他们的数据一定不会在同一个BLOCK里。而我们有会经常对这两个表做关联查询,比如说:select * from emp,dept whereemp.deptno = dept.deptno.仔细想想,查询主要是对BLOCK的操作,查询的BLOCK越多,系统IO就消耗越大。如果我把这两个表的数据聚集在少量的BLOCK里,查询效率一定会提高不少。
比如我现在将值deptno=10的所有员工抽取出来,并且把对应的部门信息也存储在这个BLOCK里(如果存不下了,可以为原来的块串联另外的块)。这就是索引聚簇表的工作原理。
-- 1. 创建一个聚簇,并指定聚簇码的数据类型,并设置相应的存储参数
-- 索引聚簇表是基于一个索引聚簇(index cluster)创建的。里面记录的是各个聚簇键。聚簇键和我们用得做多的索引键不一样,索引键指向的是一行数据,聚簇键指向的是一个ORACLE BLOCK。我们可以先通过以下命令创建一个索引簇。
create cluster clu_xxx (sno char);
-- 2. 在该聚簇上创建索引
-- 聚簇索引的任务是拿到一个聚簇键值,然后返回包含这个键的块的块地址。实际上这是一个主键,其中每个聚簇键值指向聚簇本身中的一个块。因此,我们请求部门10的数据时,Oracle会读取聚簇键,确定相应的块地址,然后读取数据
create index idx_xxx on cluster clu_xxx;
-- 3. 在该聚簇之上创建表
create table t_xxx
(
sno char;
...
)
cluster clu_xxx(sno);
SIZE 测试控制着每块上聚簇键的最大个数。这是对聚簇空间利用率影响最大的因素。如果把这个SIZE设置得太高,那么每个块上的键就会很少(单位BLOCK可以存的聚簇键就少了),我们会不必要地使用更多的空间。如果设置得太低,又会导致数据过分串链(一个聚簇键不够存放一条数据),这又与聚簇本来的目的不符,因为聚簇原本是为了把所有相关数据都存储在一个块上。
序列
不占用实际存储空间
必须要有create sequence 系统权限
create sequence seq_xxx
[start with n] -- 默认递增序列的起始值是minvalue,递减...maxvalue
[increment by n] -- 默认1
[minvalue n]
[maxvalue n]
[cache n | nocache] -- 是否预分配,存储在内存中;默认20
[cycle | nocycle]
[order | noorder]; -- 按序产生序列
-- 修改
-- PS: 不能修改start with参数
-- 必须拥有 alter 权限
alter sequence seq_xxx
maxvalue 100
...;
drop sequence seq_xxx;
create sequence seq_xxx
maxvalue 999
start with 1
increment by 10
cache 50;
insert into xxx values(seq_xxx.nextval, ...)
select swq_xxx.currval from dual;
-- 没用过的话报错ORA-08002: 序列 SEQ1.CURRVAL 尚未在此会话中定义
数据库连接
一个数据库与另一个数据库的通信路径
create [public] database link db_xxx
connect to user_xxx identified by pw_xxx
using 'connect_str_xxx'
/*
USING 'connect string'
Specify the service name of a remote database. If you specify only the database name, then Oracle Database implicitly appends the database domain to the connect string to create a complete service name. Therefore, if the database domain of the remote database is different from that of the current database, then you must specify the complete service name.
*/
drop [public] database link db_xxx;
-- 创建一个本地用户都可以访问的数据库链接,连接到 远程的数据库Training上
create public database link testlink.mydomain.com connect to trainee IDENTIFIED BY t123456
USING 'training'
select * from t_xxx@testlink.mydomain.com;
同义词
是表、视图、对象等模式对象的别名
分为私有~与公有~
公有~必须有create public synonym权限
私有~必须有create synonym权限
若在其他模式创建私有~,则必须有create any synonym权限
create [public] synonym syn_xxx for xxx;
drop [public] synonym syn_xxx;
视图
权限:create view create any view
1. 标准视图
-- 创建
create [or replace] view v_xxx 列1别名, 列2别名...
as 查询语句
[with check option[constraint con_xxx]]
[with read only]
-- 若不指定别名,默认以查询的列名为列别名
-- 若查询含函数或表达式,必须定义列别名
-- 函数指集合函数等
-- with check option: prevents visible rows from being updated to nonvisible rows
-- 管理
-- 若修改了基本表的定义,则需重新编译
alter view v_xxx compile;
-- 删除
drop view v_xxx;
可更新的视图
Oracle有一些适用于可更新联接视图的规则和限制。 其中之一是键保留表
键保留表是与视图中的行通过主键或唯一键具有一对一行关系的基表
所有可更新的列必须是键保留表中的列
增删改操作在同一时刻只能修改视图的一个基表,否则要通过instead of 触发器
键保留表的理解是:一个复杂视图,若需要出现键保留表的话则必须保证基表中至少有一张表是有主键的!(如果两个没有主键表进行关联时是不会出现键保留表的,已经验证;另外不是如果视图中有一张基表具有主键,就一定会出现另一张基表成为键保留表的现象)
其次,这两张表在进行关联时(可以是表连接也可以是多表查询,但一定要有关联条件,其关联条件其实相当于两表的主外键关系),如果关联条件是使用了主键的话,则外键表为键保留表。
A table is key preserved if every key of the table can also be a key of the result of the join. It is not necessary that the key or keys of a table be selected for it to be key preserved.
It is sufficient that if the key or keys were selected, then they would also be key(s) of the result of the join.
如果某一个表的主键可以作为这个join结果(view通常是几个表的join结果)的主键,那么这个表就是key preserved table.
这个表的主键并非一定要出现在select出来的结果集中(select list里面),但是如果其出现在结果集中,那么它必须可以满足作为这个结果集的主键的要求.
以下是可更新连接视图限制的一些示例:
- SQL语句(例如,INSERT,UPDATE 和 DELETE)仅允许修改单个基表中的数据。
- 对于
INSERT语句,INTO子句中列出的所有列必须属于保存键的表。 - 对于
UPDATE语句,SET子句中的所有列必须属于保留键的表。 - 对于
DELETE语句,如果连接生成多个保留键的表,则Oracle将从FROM子句的第一个表中删除。
除了这些限制之外,Oracle还要求定义查询不包含以下任何元素:
- 聚合函数例如,
AVG,COUNT,MAX,MIN和SUM。 DISTINCT运算符。GROUP BY子句。HAVING子句。- 集合运算符,例如
UNION,UNION ALL,INTERSECT和MINUS。 START WITH或者CONNECT BY子句ROWNUM伪列
-- 例子
create table dept(deptid int primary key,deptname varchar2(20));
create table employee(empid int primary key,empname varchar2(20),deptid int);
insert into dept values(1,'dept1');
insert into dept values(2,'dept2');
insert into dept values(3,'dept3');
insert into employee values(1,'emp1',1);
insert into employee values(2,'emp2',1);
insert into employee values(3,'emp3',2);
create view testv
as select d.deptid deptid,deptname,empid,empname,e.deptid edeptid
from dept d join employee e
on d.deptid=e.deptid;
select * from testv;
DEPTID DEPTNAME EMPID EMPNAME EDEPTID
---------- -------------------- ---------- -------------------- ----------
1 dept1 1 emp1 1
1 dept1 2 emp2 1
2 dept2 3 emp3 2
-- 在testv这个视图中,employee就是一个key preserved table,而dept不是.
-- In this view, EMP is a key-preserved table, because EMPNO is a key of the EMP table, and also a key of the result of the join. DEPT is not a key-preserved table, because although DEPTNO is a key of the DEPT table, it is not a key of the join.
-- 那么这个视图可以进行的DML为
delete from testv where empid=1
-- (操作的结果是将employee表中的empid=1的记录delete了,dept表不会有改变)
delete from testv where deptid=1
-- (操作的结果是将employee表中的empid=1和2的记录都delete了,dept表不会有改变)
update testv set empname='empx' where edeptid=1
update testv set empname='empx' where empid=1
update testv set empname='empx' where deptid=1
insert into testv(empid,empname,edeptid) values(4,'emp4',2)
-- 这个视图不可以进行的DML为
-- update testv set deptname='deptx' where deptid=1
-- update testv set deptname='deptx' where empid=1
-- insert into testv(deptid,deptname) values(4,'dept4')
-- ORA-01779: cannot modify a column which maps to a non key-preserved table
-- PS 一个View中可以有多个key preserved tables
-- 如何查看那些字段可以插入更新
select * from USER_UPDATABLE_COLUMNS where table_name='TESTV'
2. 内联视图
一种临时视图,不存在数据字典中
查询中包含临时的内联视图时,视图中的SELECT语句 先被执行,得到一个结果集,然后由外层查询语句查 询内联视图的结果。
select * from t_xxx t1, (select * from t_yyy t2) where ..
3. 物化视图
- 能够提高查询速度,这主要是因为物化视图存储了实际的数据
- 具有查询重写功能
- 物化视图具有实体表,也可以在上面建立索引
两种刷新方式
ON COMMIT: 在基表做提交操作时刷新物化视图- 可以手工通过DBMS_MVIEW.REFRESH等方法来进行刷新,也可以通过JOB定时进行刷新,即更新物化视图,以保证和基表数据的一致性;一般配合 start with 参数按照特定的时间计划,按计划更新数据,比如每天晚上12点或每周更新一次物化视图中的数据
ON DEMAND: 按需刷新,手动刷新,或者是定时刷新
刷新量的限制
COMPLETE完全刷新- 删除表中所有的记录(如果是单表刷新,可能会采用
TRUNCATE的方式),然后根据物化视图中查询语句的定义重新生成物化视图。 FAST增量更新- 只将自上次刷新以后对基表进行的所有操作刷新到物化视图中去。FAST必须创建基于主表的视图日志。对于增量刷新选项,如果在子查询中存在分析函数,则物化视图不起作用。
FORCE自动选择- Oracle会自动判断是否满足快速刷新的条件,如果满足则进行快速刷新,否则进行完全刷新。
Oracle默认为FORCE和DEMAND
设置REFRESH ON COMMIT的物化视图不能访问远端对象
在建立物化视图的时候可以指定ORDER BY语句,使生成的数据按照一定的顺序进行保存。不过这个语句不会写入物化视图的定义中,而且对以后的刷新也无效
create materialized view v_xxx
refresh [fast | complete | force]
[
on [commit | demand]
|
start with (start_time) next (next_time)
]
[build immediate | build deferred]
as
查询语句
create materialized view v_xxx
refresh force
on demand
start with sysdate next to_date( concat( to_char( sysdate+1,'dd-mmyyyy'),' 22:00:00'),'dd-mm-yyyy hh24:mi:ss')
AS
select * from table_name;
索引
create index create any index
1. 创建索引
B树索引:见PDF
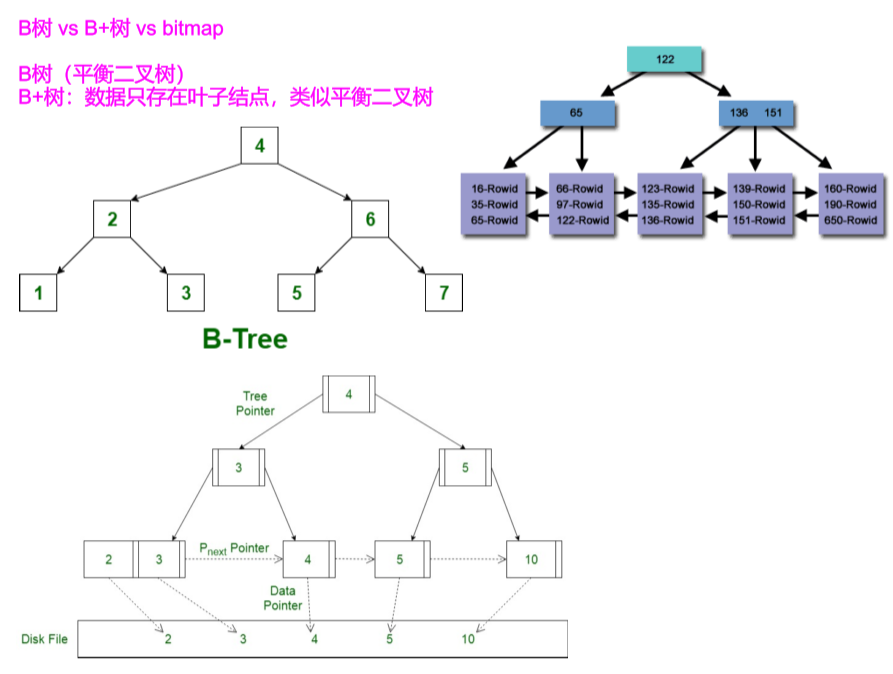
| S.NO | B tree | B+ tree |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | All internal and leaf nodes have data pointers | Only leaf nodes have data pointers |
| 2. | Since all keys are not available at leaf, search often takes more time. | All keys are at leaf nodes, hence search is faster and accurate.. |
| 3. | No duplicate of keys is maintained in the tree. | Duplicate of keys are maintained and all nodes are present at leaf. |
| 4. | Insertion takes more time and it is not predictable sometimes. | Insertion is easier and the results are always the same. |
| 5. | Deletion of internal node is very complex and tree has to undergo lot of transformations. | Deletion of any node is easy because all node are found at leaf. |
| 6. | Leaf nodes are not stored as structural linked list. | Leaf nodes are stored as structural linked list. |
| 7. | No redundant search keys are present.. | Redundant search keys may be present.. |
AD
- 数据一定在叶子结点出现
- 左孩子严格小于,右孩子可大等于
The definition of order for a tree would be the maximum branching factor, i.e. the maximum number of children that a node may have
假设有order=m,则
- 每个中间节点的孩子数取值范围为[[m/2](上取整), m]
- 每个节点存储的key数量取值范围为[[m/2]-1, m - 1]
| Node Type | Children Type | Min Number of Children | Max Number of Children |
|---|---|---|---|
| Root Node (when it is the only node in the tree) | Records | 0 | m-1 |
| Root Node | Internal Nodes or Leaf Nodes | 2 | m |
| Internal Node | Internal Nodes or Leaf Nodes | ${\displaystyle \lceil m/2\rceil }$ | m |
| Leaf Node | Records | ${\displaystyle \lceil m/2\rceil }$ | m |

假设order=4
插入1,4,7,10并变形
插入17,21并变形
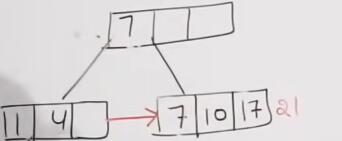
变形结果
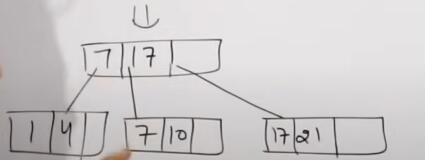
插入31,25,19,20并变形
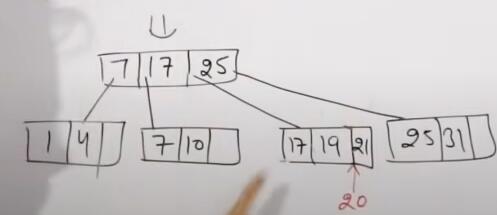
变形结果
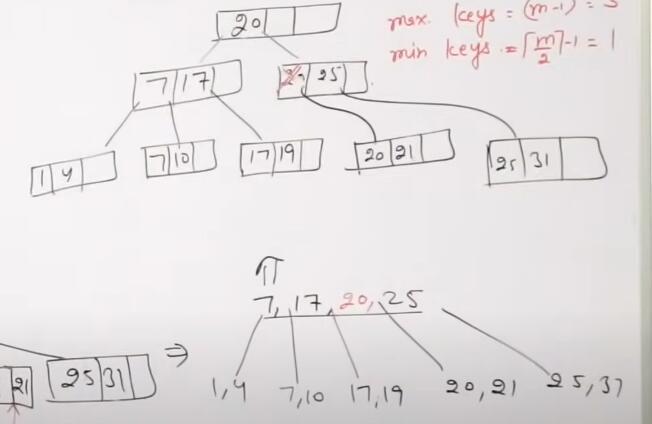
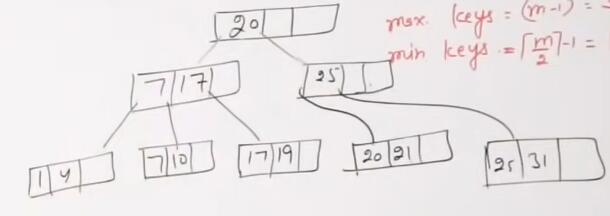
最终结果
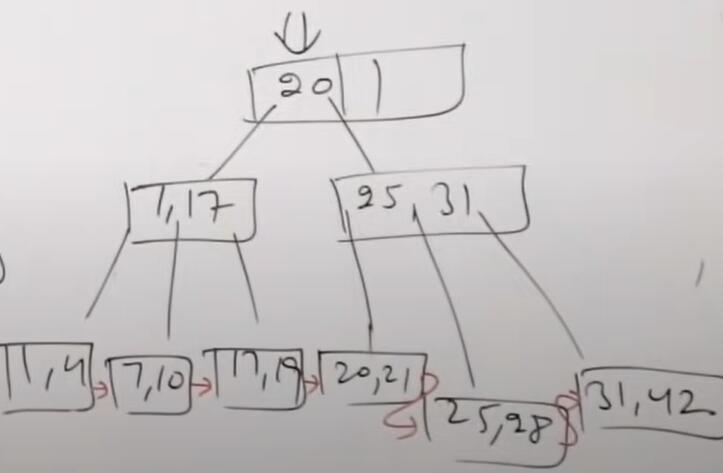
位图索引:见笔记
- 缺点:不经常做update(所以一般用在数据仓库)
- 优点:节省空间
函数索引:对col使用函数;若查询条件包含相同的函数,则会使用它
-- B树索引
create index idx_xxx on t_xxx(col1, col2);
create index idx_xxx on t_xxx(col1 ASC, col2 DESC);
-- 位图索引
create bitmap index idx_xxx on t_xxx(同上)
-- 函数索引
create index idx_xxx on t_xxx(lower(col))
2. 修改索引
alter any index 或在相应表上index对象权限
一般用于碎片太多的情形
-- 合并索引
alter index idx_xxx coalesce deallocate unuserd;
-- 重建索引
alter index idx_xxx rebuild;
3. 删除索引
drop index drop any index
drop index idx_xxx;
分区表
索引分区一样,可见课本
1. 基于范围的分区
create table t_xxx
(...)
partition by range(col_list)(
partition par_01 values less than value_list1,
partition par_03 values less than value_list1
);
-- Example
create table t_xxx(...)
partition by range(ID)(
partition par_01 values less than (100) tablespace ts1,
partition par_02 values less than (MAXVALUE) tablespace ts2,
);
-- PS MAXVALUE是关键字
-- 多个列时需同时满足
-- less than是指严格小于(字面意识)
CREATE TABLE t_test(
ID INT
)
PARTITION BY RANGE(ID)(
PARTITION P1 VALUES LESS THAN(10),
PARTITION P2 VALUES LESS THAN(20),
PARTITION P3 VALUES LESS THAN(30)
);
insert into t_test values(9);
insert into t_test values(10);
insert into t_test values(11);
-- insert into t_test values(30);
-- ORA-14400: 插入的分区关键字未映射到任何分区
SELECT ID, DO.SUBOBJECT_NAME
FROM t_test TI, DBA_OBJECTS DO
WHERE DBMS_ROWID.ROWID_OBJECT(TI.ROWID)=DO.OBJECT_ID;
ID SUBOB
--- -----
11 P2
10 P2
9 P1
alter table t_test drop partition P2;
select * from t_test;
ID
---
9
2. 基于散列的分区
使得数据均匀分布在磁盘上
create table t_xxx (...)
partition by hash(id) (
partition par_01 tablespace ts_1,
partition par_02 tablespace ts_2
);
-- 或
create table t_xxx (...)
partition by hash(id)
partitions 2
store in (ts1, ts2);
3. 基于列表的分区
范围分区的离散情况
分区关键字只能为单列
create table t_xxx(...)
partition by list(major) (
partition par_01 values('数学', '语文'),
partition par_02 values('英语', '日语')
)
4. 组合分区
首先对表进行范围分区,再进行散列或列表分区
-- 范围-散列组合分区
-- 看PDF,下面有问题
create table t_xxx(...)
partition by range(timestamp)
subpartition by hash(id) (
partition par_01 values less than(to_date(,,,)),
partition par_01 values less than(to_date(,,,))
)
-- 范围-列表组合分区
create table t_xxx(...)
partition by range(timestamp)
subpartition by list(major) (
partition par_01 values less than(to_date(,,,)) (
subpartition par_11 values('语文'),
subpartition par_12 values('数学'),
)
partition par_02 values less than(to_date(,,,)) (
subpartition par_21 values('语文'),
subpartition par_22 values('数学'),
)
)
5. 表分区操作
-- 查看指定分区的数据
select * from t_xxx partition(par_01);
select * from t_xxx partition(par_01) ss where ss.id=..;
-- 复制表分区
create table t_xxx as select * from t_yyy partition(par);
-- 增加范围分区
-- 使用MAXVALUE时不可增加分区
alter table t_xxx add partition par_01 values less than(...) [tablespace ts_xxx];
-- 增加列表分区
alter table t_xxx add partition par_01 values '数学' [tablespace ts_xxx];
-- 分区重命名
alter table t_xxx rename partition par_xx to par_yy;
-- 合并hash分区
alter table t_xxx coalesce partition;
-- 合并复合分区:合并某个子分区到其他子分区
alter table t_xxx modify coalesce subpartition;
-- 合并第三个分区到第四个分区
alter table t_xxx merge partitions par_03, par_04 into partition par_04;
-- 删除分区:drop保留全局索引
alter table t_xxx drop partition par_xxx;
-- 若有全局索引,需重建索引
alter index idx_xxx rebuild;
-- 删除分区:先delete分区表所有数据+再alter drop
delete from t_xxx where ...>=to_date(...);
alter table t_xxx drop partition par_xxx;
-- 删除具有完整性约束的分区
-- 法一:禁用约束+删除
alter table t_xxx disable constraint cnt_xxx;
alter table t_xxx drop partition par_xxx;
alter table t_xxx enable constraint cnt_xxx;
-- 法二:先删除行,再删除分区
delete from t_xxx where ...>=to_date(...);
alter table t_xxx drop partition par_xxx;
-- 移动分区数据
alter table t_xxx move partition par_xxx tablespace ts;
-- 拆分分区
alter table t_xxx split partition par_00 at(break_xxx) into (partition par_01, partition par_02);